Our Explainable
AI Approach
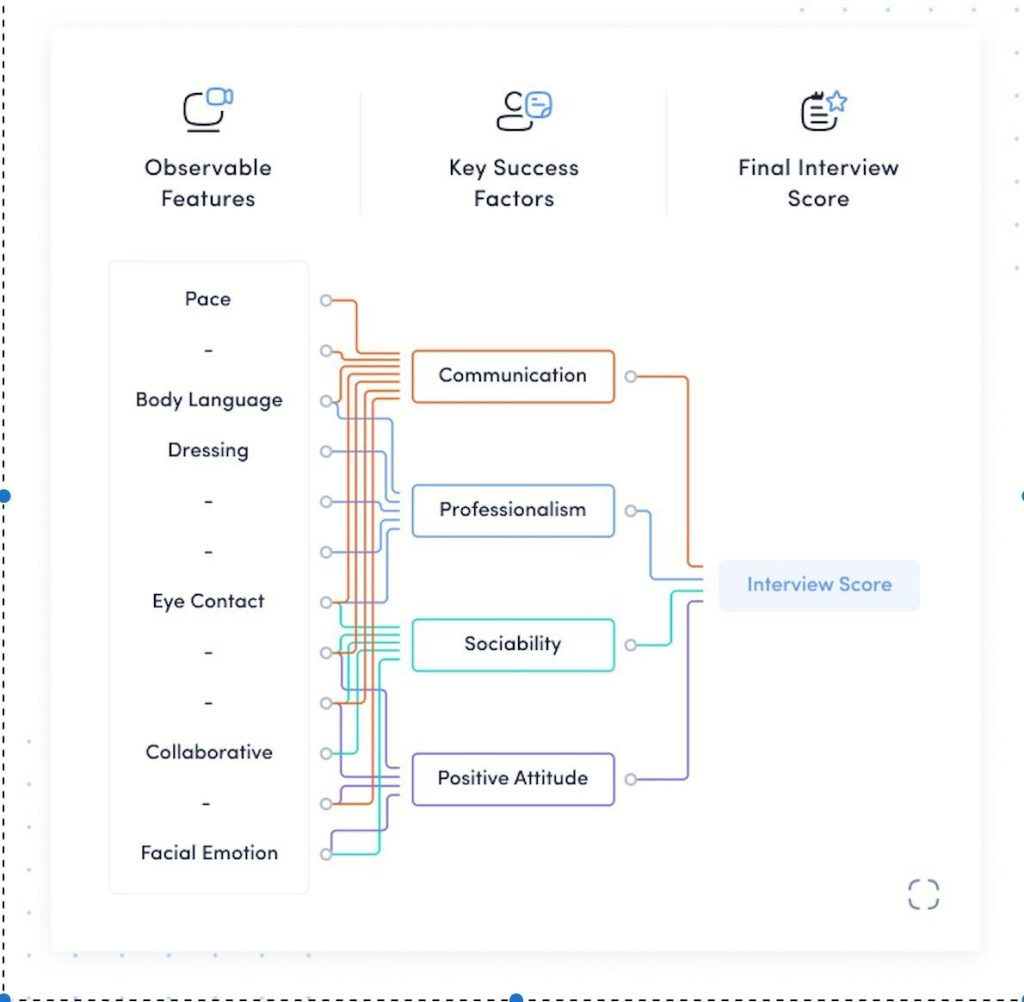
At Interviewer.AI, we build Explainable AI[1] to help teams identify desirable talents in their talent acquisition processes. Having an Explainable AI framework allows us to provide insights on the key performance factors of candidates and minimize the risk of prejudice judgements that may arise from black-box AI approaches.